Parachutist training first began in North Korea in the early 1960s and by 1968 there were at least two known airborne units. From then until the death of Kim Jong Il, training centers had been established in Koksan, Pyongyang (Songsin District), Sangwon, Taetan, Taechon, and Unsan.
Under Kim Jong Un, four new ones have been constructed and three of the older facilities have undergone new construction and other improvements.
Map of North Korea's parachutist training centers. | Image: Jacob Bogle
Today, these ten facilities aid in training the seven known paratrooper units in the country. Four units are part of the Korean People's Army and three brigades are under the KPA Air Force.
Army
26th Air Landing Brigade
38th Air Landing Brigade
45th Air Landing Brigade
525th Special Operations Battalion
Air Force
11th Airborne Snipers Brigade
16th Airborne Snipers Brigade
21st Airborne Snipers Brigade
According to Joseph P. Bermudez' 2001 book Shield of the Great Leader: the armed forces of North Korea, within the various special forces units there are three airborne brigades, three air force sniper brigades, and five other sniper brigades that may or may not take part in parachute training. The six airborne and air force brigades he mentions total 21,000 personnel.
Whether the addition of new training sites under Kim Jong Un reflects the creation of new military units, the transfer of personnel from non-airborne units to existing airborne units, to aid in training other related and auxiliary troops, or simply a desire to improve overall training capacity, I don't know.
What is clear, however, is that North Korea is placing a great deal of importance on both their special operations forces in general and specifically on airborne (be they special forces or not).
Some of the training facilities are very near airbases while others are not. This could reflect which ones are attached to the KPA Air Force and which ones are Army.
I also want to stress that airborne forces are only one prong of North Korea's elite and special forces. As well as being delivered by air, they can infiltrate South Korean targets by
hovercraft, submarine, other landing craft, and even tunnels.
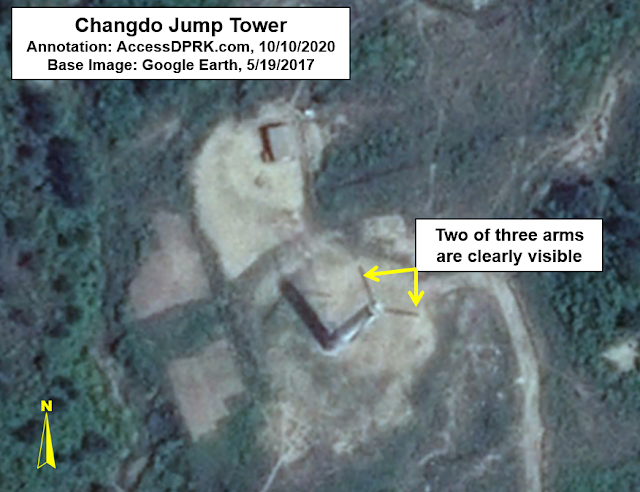
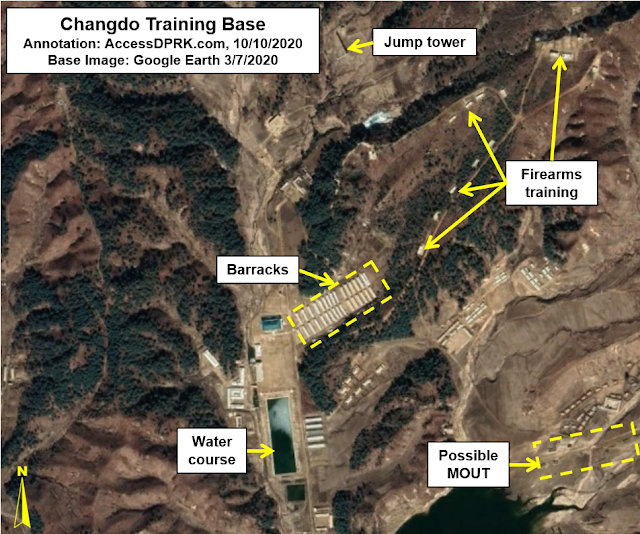
Changdo (38.650° 127.745°)
Changdo is located in Kangwon Province, about 36 km from the DMZ. It is a large training base surrounded by mountains and has existed for decades. However, in 2014 a "jump tower" was added to go along with numerous firearms ranges. Additionally, from 2012 to 2019, twenty-two new barracks buildings were constructed, and other changes were made to the base as well.
In keeping with the
upgrades of North Korea's nuclear
and conventional forces, an apparent urban warfare training site (or
MOUT, military operations on urban terrain) was built in 2019 in the southeast of the base. Presently, the whole base covers over 5.6 sq. km.
Traditionally, these towers are between 11 and 61 meters in height. The smaller ones are basically used for someone to jump off of a raised structure while strapped to a harness to experience the sensation of a jump, while the taller ones are high enough for a parachute to expand and are used by troopers during the last portion of their training before jumping out of a real aircraft.
I haven't been able to positively identify any of the smallest towers or other structures like the lateral drift apparatus. I have come across a few examples that may be them, but I am not certain. As such, I will only be pointing out the larger towers.
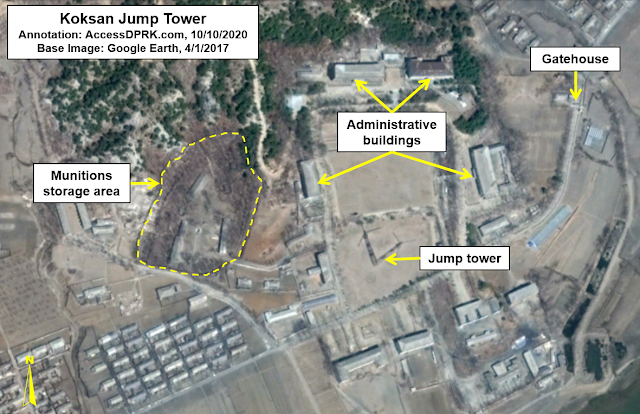
Koksan (38.658° 126.666°)
The Koksan training base is located in an area with multiple runways of varying types. The most important is Koksan Airbase 6 km to the west of the training base. There is also the Chik-tong Airfield, an auxiliary runway adjacent to Koksan AB, two additional airfields, and two
emergency highway strips.
Only the Koksan AB has a paved runway, the rest are simply grass fields or compacted dirt (such as the highway airstrips). While these other landing strips aren't meant for regular fighter jet use, they can all accommodate the country's large fleet of An-2 biplanes. These Soviet-built planes can fly low, have a small radar cross-section, and are a keystone for North Korea's special forces.
The idea behind having these antiquated planes is to allow reconnaissance and to infiltrate behind enemy lines during the opening stages of a new war.
"During the dark of night, as part of the opening throws of a battle royale between South Korea, the U.S. and North Korea, hundreds of these old radial engine biplanes will fly low over the ground at slow speed, penetrating deep into South Korean airspace. For the vast majority of their crews it will be a one-way mission—to deliver Kim Jong Un's hardest shock troops deep behind enemy lines. This is done via low altitude air drop, as seen above, or by landing in short stretches of fields or roadways." -- Tyler Rogoway,
The Drive
The Koksan training base's proximity to all of these runways makes a lot of sense regarding training parachutists to operate on a wide range of landing sites and terrains (as the area has low-lying mountains, open agricultural plains, and even small reservoirs that could assist in training for water landings).
A closeup of the jump tower. Its lattice structure can clearly be seen and the three arms from which recruits are dropped to the ground (landing zones) are also visible.
In contrast to the concrete tower at Changdo, Koksan's tower is a steel lattice tower, like the one pictured at Fort Benning. Only one of the newly built towers is also a steel lattice. The rest are concrete. This reflects a trend to either build concrete towers or to modify the older steel towers (as was the case with Taetan and Unsan).
Pyongsan (38.400° 126.373°)
Similar to Changdo, the tower at Pyongsan lies within an older (and large) training facility. The concrete tower was constructed in 2015 and it is within a section of the base that includes water obstacles and an urban warfare training site (MOUT).
The whole base occupies approximately 10.2 sq. km. and has a substantial administrative section, a driver training section, and apparent economic facilities (like farming and making agricultural products).
The military is heavily involved in the country's economy and, in effect, creates its own parallel economy to the national one. So it is not unusual for large bases to be involved in either
farming or manufacturing with intent to sell their products overseas to earn hard currency for the regime. And nearly every military site, large and small, has converted some of their land into farms to help feed the people stationed there.
The nearest major airbase to Pyongsan is Nuchon-ni, some 29 km to the southwest. That, the fact that there is a MOUT facility within the base, and the driver training area all lead me to suspect that this is one of the Army's facilities and not the Air Force. If it is within the Army, it would be subordinate to KPA IV Corps which has responsibility for the western half of North Hwanghae Province and South Hwanghae Province.
Pyongyang-Songsin (39.001° 125.815°)
The site in Pyongyang is unique because it is located in an urban area. Two km away from the former Mirim Airfield and 6 km away from Kim Il Sung Square, the tower is located within a small training facility that occupies only 11.8 hectares.
Unfortunately, I know very little about this base. Is it for training special forces? Is it part of the capital's defense corps? Perhaps it is used to train members of the
Supreme Guard Command, the 200,000-man strong bodyguard force that protects the Kim family? I just don't know.
Very little has changed at the base since 2000 (the earliest available image on Google Earth) but it has been well maintained, suggesting that it has been in continual use.
Sangwon (38.903° 125.967°)
Sangwon, in a small town within the larger Pyongyang region, is predominantly for jump training, although there are some smaller components to the base. Being within Pyongyang, it is surrounded by numerous other military bases including three other training facilities within 2.5 km of the airborne facility.
It is likely that Sangwon falls under the Army, and potentially the 38th Air Landing Brigade which is based in Pyongyang. Pyongyang is defended by a complex network of forces. The Supreme Guard Command, while tasked with keeping the Kim family and palaces safe, also coordinates with the Pyongyang Defense Command, III Corps, the Pyongyang Air Defense Command (as part of the Air Force), and the various internal police agencies. In all, this provides up to 350,000 soldiers and police stationed in and around the capital (many of the Supreme Guard's 200,000 men are not within Pyongyang, perhaps half are stationed across the country at various palaces).
Sangwon covers approximately 1.98 sq. km. The tower is concrete, and the facility has not undergone any substantial upgrades since at least 2006.
An interesting note is that Sangwon is less than 5 km away from a replica of the Blue House (South Korea's presidential residence) which was constructed in 2016, and was the site of a
training exercise involving both paratroopers and other special operations forces storming the mock residence.
Sonchon (39.823° 124.918°)
Sonchon was constructed sometime between 2014 and 2017 (there's a gap in images for the intervening years) and is a traditional steel lattice tower, but unlike most of the others, it only has two drop arms instead of three. If it is part of the Air Force, it would likely be under the 1st Air Combat Command headquartered at Kaechon. In the event it is Army, it would be controlled by VIII Corps.
As mentioned earlier, this site was first brought to the public's attention (as far as I am aware) by
Nathan Hunt in July 2020. One reason for why it may have gone largely unnoticed is that it is neither part of a major training base nor is it close to a major airbase (the closet being Panghyon in Kusong, 26 km to the northeast). However, it is also 20 km from Kwaksan AB. Kwaksan is a secondary air base, but it does have a wing of between 50-60 An-2s stationed there.
Although the training base is small and fairly nondescript at first glance, it happens to contain an underground facility (UGF), which makes the addition of a jump tower curious as they are seemingly unrelated structures.
The Sonchon underground facility doesn't appear to be part of manufacturing, so it's likely storage. Over the years some minor changes have been made to the site but this image from 2010 most clearly shows the berms and entrances.
Taetan (38.159° 125.222°)
Named after the Taetan Airbase (aka T'aet'an-pihaengjang Airbase) that is just 3.3 km away across a range of hills, Taetan is one of the older training bases that has undergone recent upgrades.
In 2015 the steel tower was clad in either steel sheeting or wood to cover up the lattice structure, and in 2019 a row of six jets was added (likely non-functional planes to aid in training and getting recruits familiar with the equipment). Additionally, several buildings were being constructed across the parade ground.
The base covers approximately 3.5 sq. km and is divided into the airborne training section and the administrative/barracks section to the right of the airborne side.
The semi-circular area around the tower is 110 meters in diameter. From the tower to the small "landing zones" where recruits drop is roughly 15 meters (the drop arms also extend 15 meters from the main tower structure).
Taetan may be closest to the Taetan AB but it is also the only jump tower in South Hwanghae Province which is under the KPA IV Corps and the KPA Air Force 3rd Air Combat Command. These top-level commands oversee the whole province (and other areas). Within the province are six additional airfields, some host fighter jets and others are only for smaller craft like the An-2. Any necessary training for personnel at the other airfields would likely be sent to Taetan.
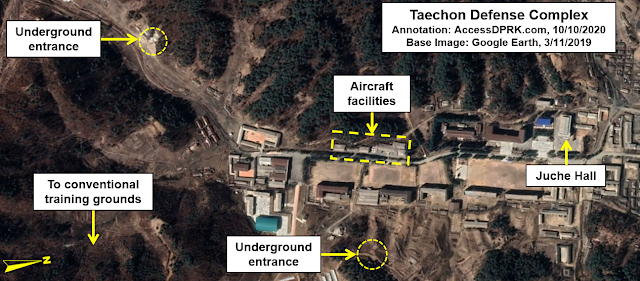
Taechon (39.864° 125.498°)
Taechon's steel lattice tower is a mere 4 km south of the Taechon Airbase which serves as the headquarters for the 5th Air Transport Division. It's a very small base but in 2018-2019, over two dozen buildings were constructed. It is also only 2.3 km away from a large military complex that has its own conventional training course.
At the larger base, historic imagery reveals various aircraft and helicopters, as well as tanks and other equipment. This suggests that the complex has both training/educational purposes and a maintenance role. There are also two underground sites within the complex.
Given the airborne training base's proximity and the larger base's involvement with aircraft, it's hard to ignore the likelihood of the two places being connected.
Unsal (40.009° 125.879°)
The concrete jump tower was built sometime between 2012 and 2014 next to the largest urban warfare training center in North Korea. The whole base covers approximately 2.75 sq. km and there are other military sites nearby.
As we see again, there is an airborne site and urban warfare site being placed together. In all, four airborne training bases have obvious MOUT training facilities as well.
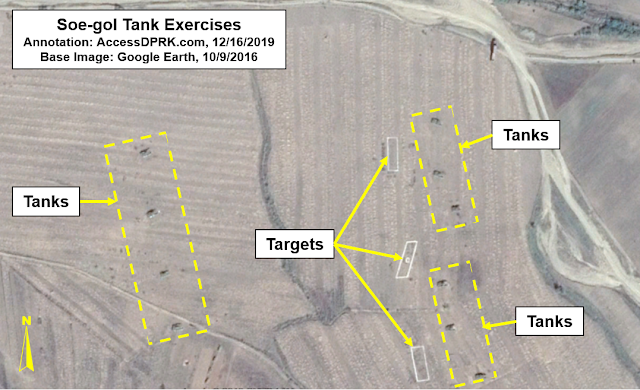
The purpose of the North Korean parachutist is to infiltrate and conduct operations behind the lines.
They "
pertain to creating total havoc deep inside South Korean territory. This includes attacking key infrastructure and military installations, and generally sowing massive terror among the already frightened South Korean populace," making their positioning within MOUT facilities a logical step.
The addition of the jump tower ca. 2014 isn't the only thing that has changed at Unsal. Around the same time, a small addition to the training grounds was added, and between 2017 and 2019 the administrative area of the base was modernized and several of the MOUT structures were demolished and replaced with apparent barracks.
Unsan (39.365° 126.052°)
As with the Taetan tower, the one in Unsan also had its lattice partially clad in either wood or steel in 2015. The landing area around the tower has a diameter of about 70 meters.
It is surrounded by numerous other training areas including shooting ranges, an equipment familiarization site (labeled "aircraft row" in the image), and it is located in between two larger military facilities. Given that all of the sites are directly connect via road (and without any security gates between them), I think it is actually one single large base approximately 4 sq. km in size.
Unsan is 14 km away from the important Sunchon and Pukchang airbases. It is also very close to an unusual defense complex. The complex has a variety of buildings with different purposes as well as equipment bunkers, possible educational buildings, and its own training grounds.
I have asked several people about the complex and no one has been able to offer a definitive identification. However, most suspect that it is either a military academy or a research and development facility. The complex and airborne training center are also connected via road.
Conclusion
The sheer number of these facilities, their association with special forces facilities, and the fact that the regime has been willing to spend new resources on their capabilities and capacities means that North Korea's airborne troops and special operations forces will continue to pose a threat to the peninsula, and will be high on the list of forces to counter during any war.
Just because their facilities and equipment seem antiquated, doesn't mean they are without teeth. Wooden biplanes can fly low, evade most radars and surface-to-air missile systems in the region, and deploy highly motivated and trained troops to any point in South Korea. The An-2 fleet doesn't require major airfields, and in fact, can take off from any compacted dirt surface that has a straight run of
487 meters, turning plenty of highways into makeshift runways. (For comparison, fighter jets can require 2,500 meters or more of runway length.)
North Korea has a history of using their special forces in all four domains (land, air, sea, and cyber) to conduct operations against South Korea including assassination attempts and sinking ROK vessels.
Having robust airborne and special operations forces will enable the North to inflict significant damage during the opening stages of a war and enable them to continually harass the military and people of South Korea even in times of "peace".
North Korea has never been one to hide their
true intentions. Be it with ballistic missiles, nuclear warheads, new submarines, or matters with their conventional forces, the country always broadcasts what their goals are.
In previous military parades, questions were raised about how "real" various weapon systems were to "just how the hell did they acquire them?" Were they real missiles or just bits of metal welded together to make for a good show? Did they build them domestically or do some creative engineering of foreign equipment?
Even with the most recent parade, questions surround the
massive new ICBM and its transporter vehicle. Other questions were asked about the
new battle tank displayed.
But each time questions are raised, the world ends up seeing fully functional systems within a year or two, not simply parade models. We see activities happening at the Sinpo submarine yard almost monthly, and after nearly a year of waiting, we received our first look at North Korea's new "strategic weapon" (now being called the Hwasong-16 ICBM).
The same must be said for the country's conventional forces. They broadcast what they're doing.
We should keep in mind that these additions to the country's arsenal have all happened in less than a decade under Kim Jong Un, and that 40% of the airborne training sites established throughout the country were done under Kim Jong Un. Many other military changes and developments have occurred, and others are being developed as I write this.
With these additions, the regime is talking. Are we listening?
I would like to thank my current
Patreon supporters: Amanda O., Anders O., GreatPoppo, John Pike, Kbechs87, Planefag, and Russ Johnson.
--Jacob Bogle, 10/15/2020