2020 brought three typhoons and massive flooding to North Korea. The combined effects of typhoons Bavi, Maysak, and Haishen destroyed large numbers of homes and thousands of hectares of farmland. The scale of the recovery efforts redirected labor and material away from large national projects like the Pyongyang General Hospital and the Tanchon Hydroelectric Project.
With a 2020 estimated population of 39,000, the city of Yonsa sits among the Hamgyong Mountain Range and is bisected by the Yonmyonsu River as it flows toward the Tumen River. This gives the city a beautiful natural landscape, but also places it at risk for floods.
In 2016 major flooding occurred along all of northern North Korea, affecting over 600,000 people and even damaged the important border cities of Hoeryong and Mansu.
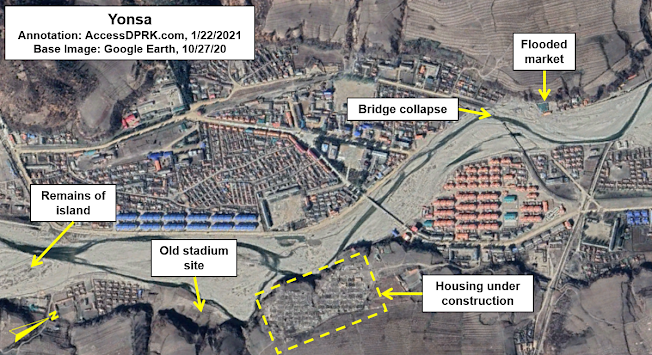
Yonsa was one of the places affected by the flooding. The river spilled its banks and destroyed the stadium, damaged the earthen flood barriers that line the riverbanks within the town, and caused other damaged along its whole course (mostly flooding farmland).
Prior to the flood, the Yonmyonsu River and its Kuunsu River tributary joined together at the terminus of a long peninsula. After the flood, that peninsula had been severed and became an island 1.58 km long and 100 acres in area. The confluence now happens at the southern end of the island instead of the northern point of the former peninsula.
In response to the damage, the authorities used the event to rebuild large parts of the town and to build more modern apartment blocks. The new island was left detached, but work was done to shore up its defenses and rebuild destroyed properties.
The apartments were constructed in two sections of town. Twelve were built in the "downtown" area and on the northern end of town, on the east bank of the river, thirteen other apartment blocks were built. These, along with seventeen other multi-family homes were constructed where a large neighborhood once stood, comprised of scores of small one- and two-family dwellings.
Several other apartments and homes were built up and down the river valley. On top of this, over 10 km of new and repaired flood barriers were built, including around the new island. Unfortunately, when their first major test came only three years later, they failed spectacularly.
Fast-forward to the 2020 Typhoon Season. In rapid succession, the country got hit by the remains of typhoons Bavi, Maysak, and Haishen. Taking a page out of his grandfather's playbook, Kim Jong Un could be seen traveling the countryside and guiding rebuilding projects.
Some of the damage to Yonsa included half of the marketplace getting washed away, the railway bridge was broken, the flood barriers built after 2016 were breached in multiple places, and 44 acres of a cooperative farm and forest management facility were flooded. Additionally, some of the apartment buildings constructed after the 2016 flood were close to having been washed away; their lower floors likely needing some repair.
While Yonsa was one of the damaged cities, Kim didn't visit. Nonetheless, clean-up and rebuilding efforts began almost immediately.
On the Oct. 27, 2020 Google Earth image, four-five dozen family homes can be seen being constructed across the southern riverbank. More work has undoubtedly taken place since then. The question is, will the new work survive any better the next time it floods than before?
One bit of very good news is that despite two large flooding events, the Sinyang Dam 10.2 km upriver, never failed. If it had, the release of its 448-acre reservoir (at least 16.3 million gallons) could have destroyed far more of the town, plus all the small houses that line the riverbanks on the way to Yonsa.
Whether or not any storm or set of storms can be attributed directly to climate change is up for debate. What isn't debatable is that the long-term impact of a changing climate is more extreme and less predictable weather. If the three relatively mild storms (none were greater than Category 1 when they hit the country) can cause so much damage that it disrupts activities going on nationwide, North Korea needs to begin planning for even worse catastrophes in the future.
In the meantime, Yonsa's small stadium has never been rebuilt.
I would like to thank my current Patreon supporters: Amanda O., Anders O., GreatPoppo, Joel Parish, John Pike, Kbechs87, Planefag, and Russ Johnson.
--Jacob Bogle, 1/23/2021
AccessDPRK.com
JacobBogle.com
Facebook.com/accessdprk
Twitter.com/JacobBogle